Tutorial 0: Static Scene#
Objective: Learn how to load and visualize a basic simulation scene with objects.
What you’ll learn:
How to create a
ScenarioCfgwith objectsHow to launch a handler and render a scene
Different object types available in MetaSim
Prerequisites: Installation completed
Estimated time: 15 minutes
Running the Tutorial#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim <simulator>
you can also render in the headless mode by adding --headless flag. By using this, there will be no window popping up and the rendering will also be faster.
Examples#
Isaac Sim#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim isaacsim
Isaac Gym#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim isaacgym
Mujoco#
# For mac users, replace python with mjpython.
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim mujoco --headless
Note that we find the non-headless mode of Mujoco is not stable. So we recommend using the headless mode.
Genesis#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim genesis
Note that we find the headless mode of Genesis is not stable. So we recommend using the non-headless mode.
Sapien#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim sapien3
Pybullet#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim pybullet
Newton#
python get_started/0_static_scene.py --sim newton
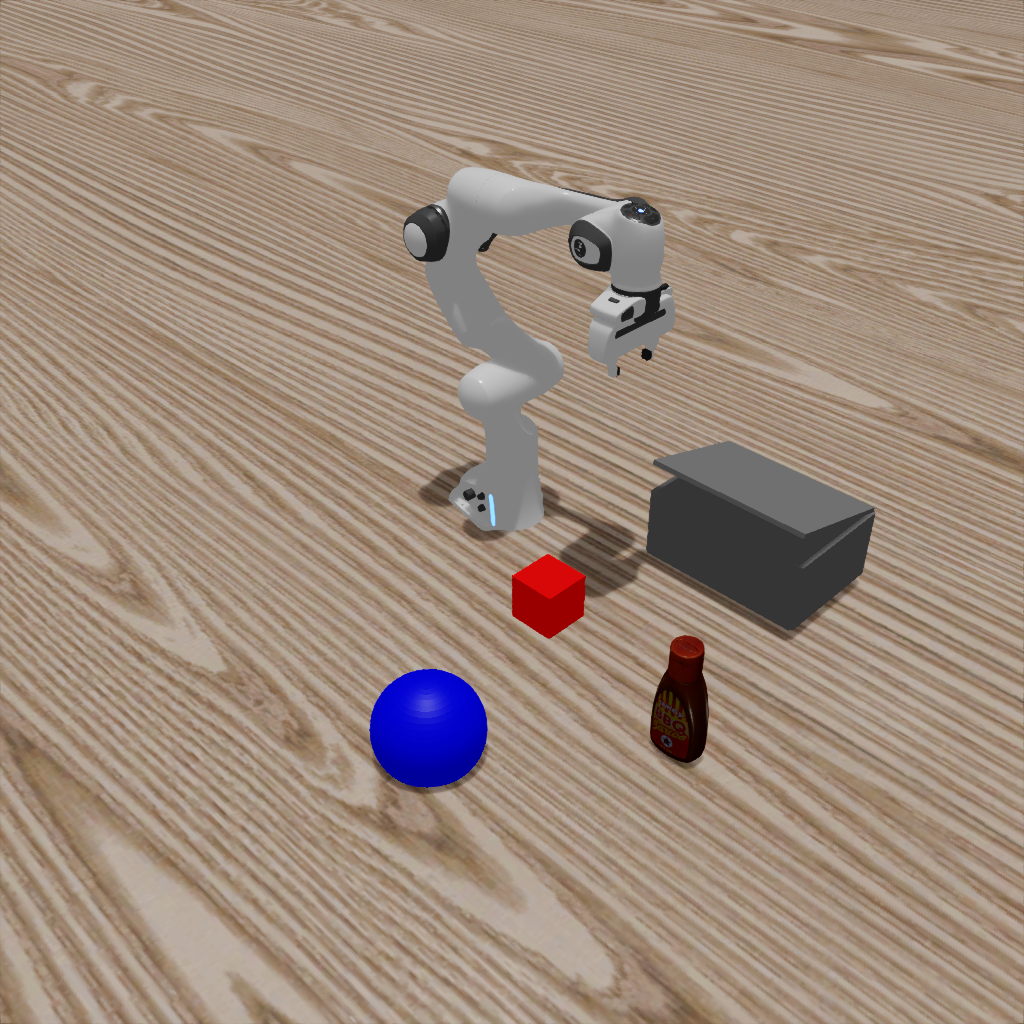
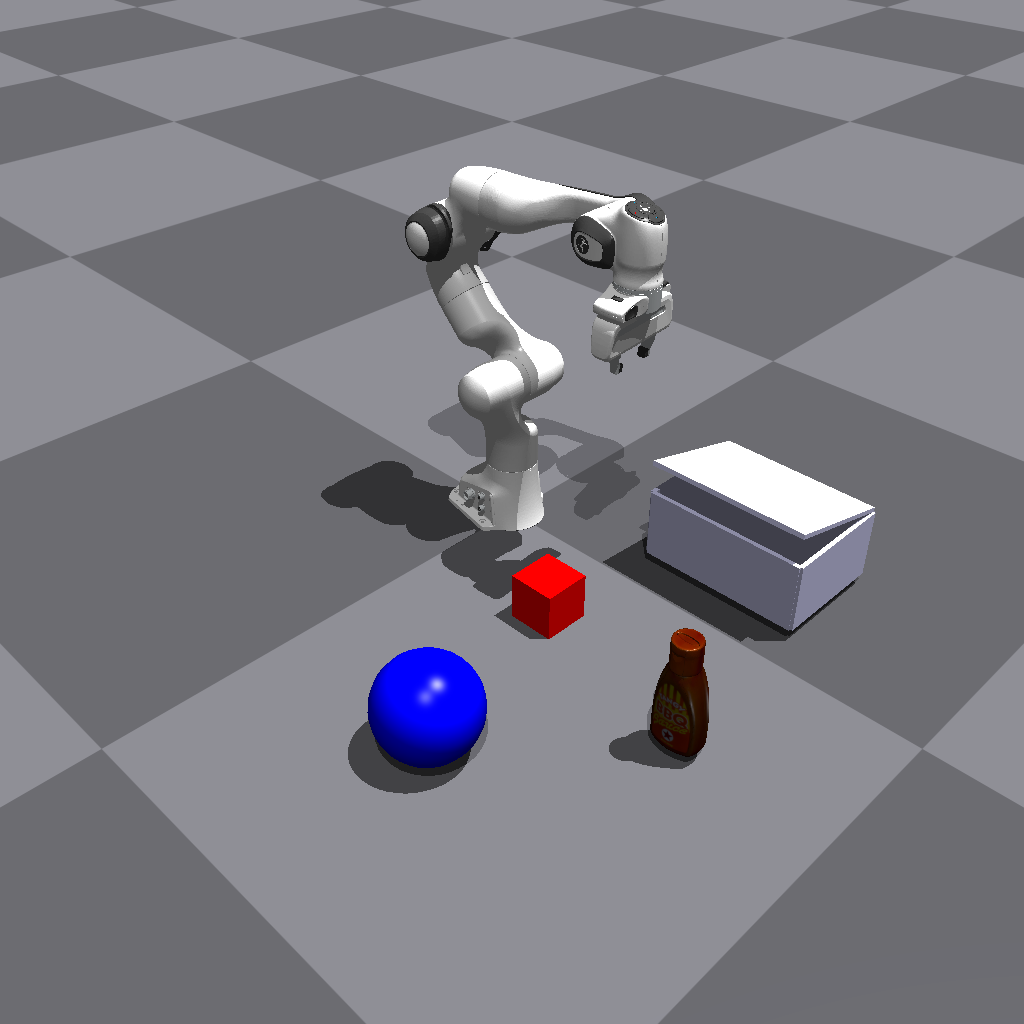
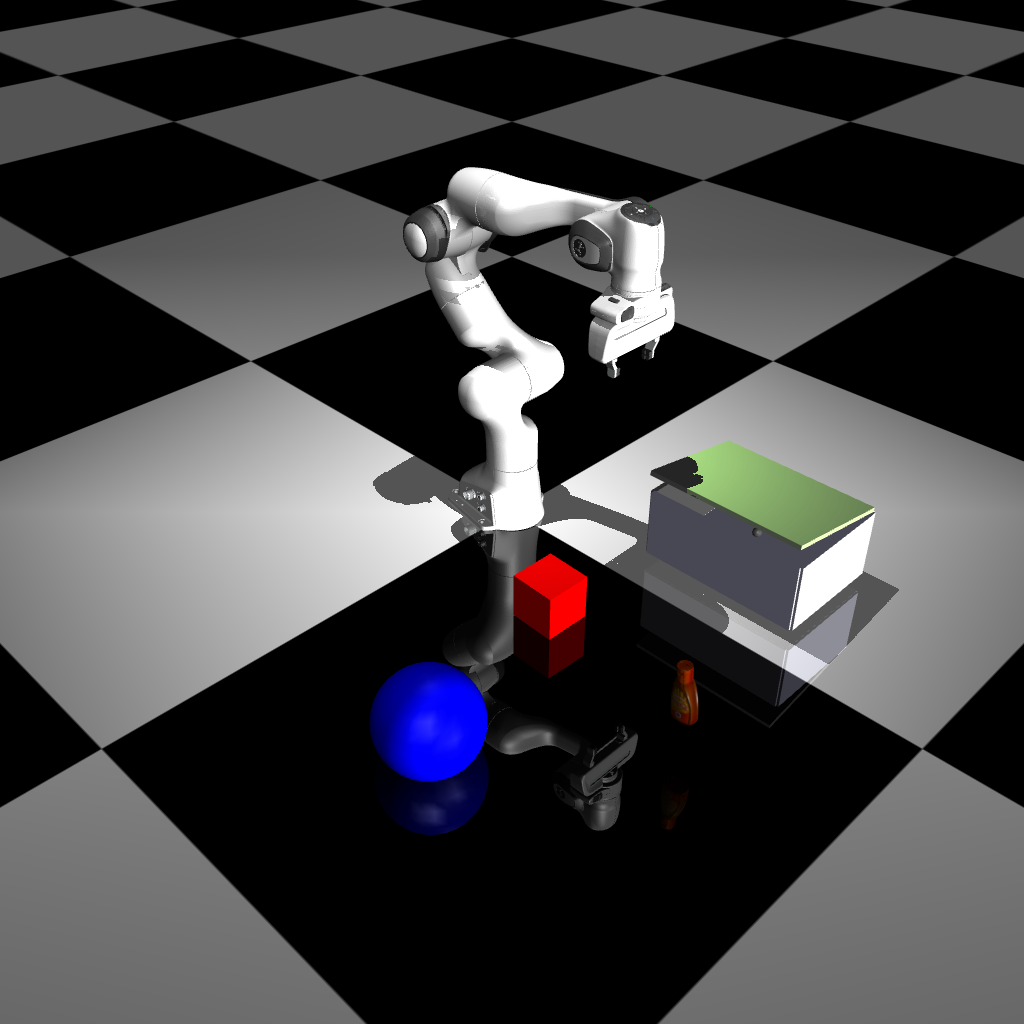
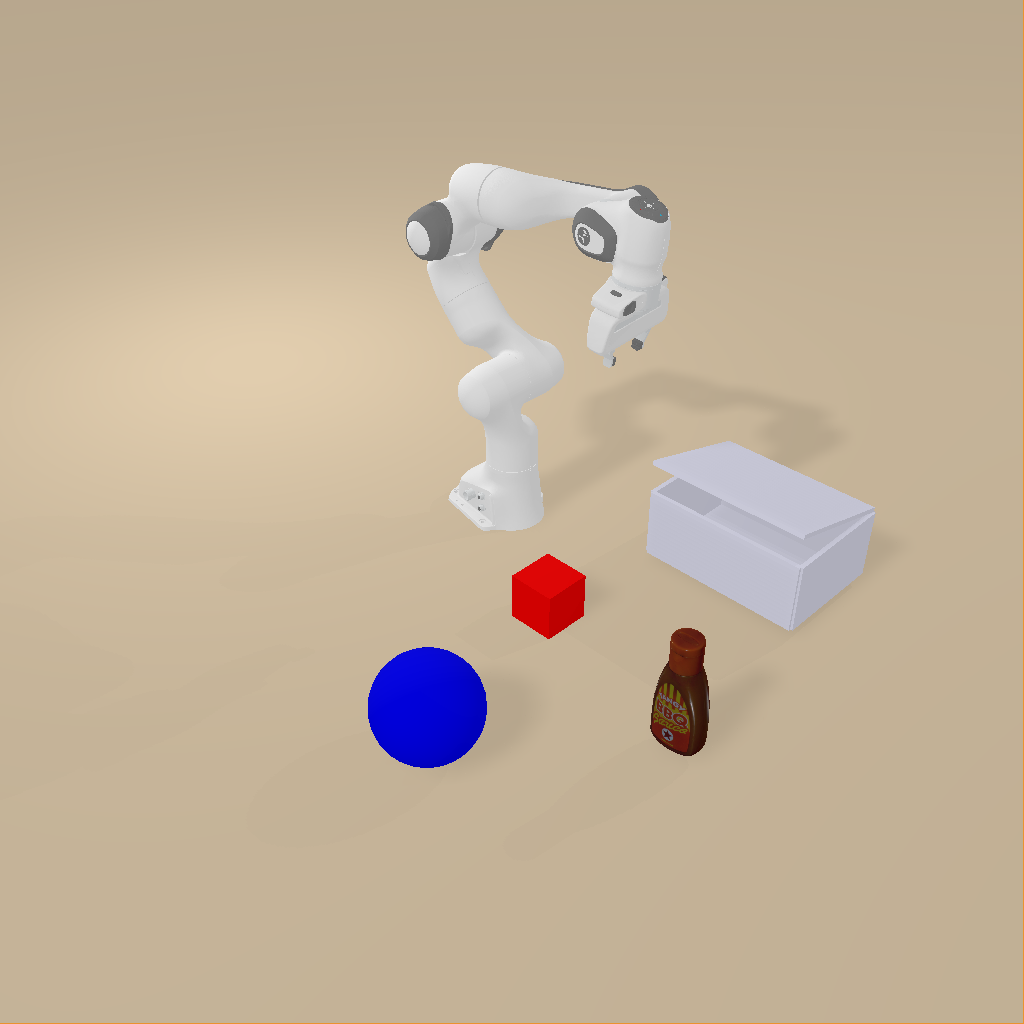
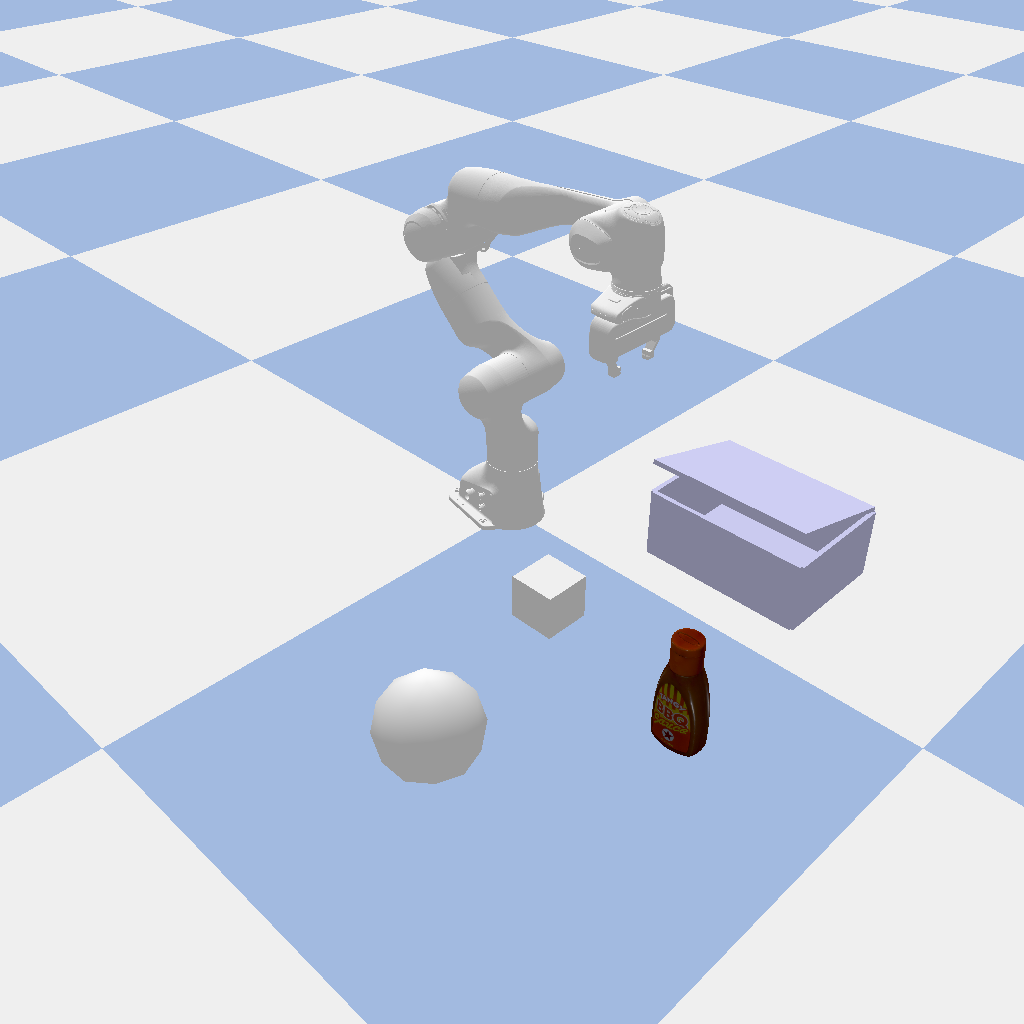
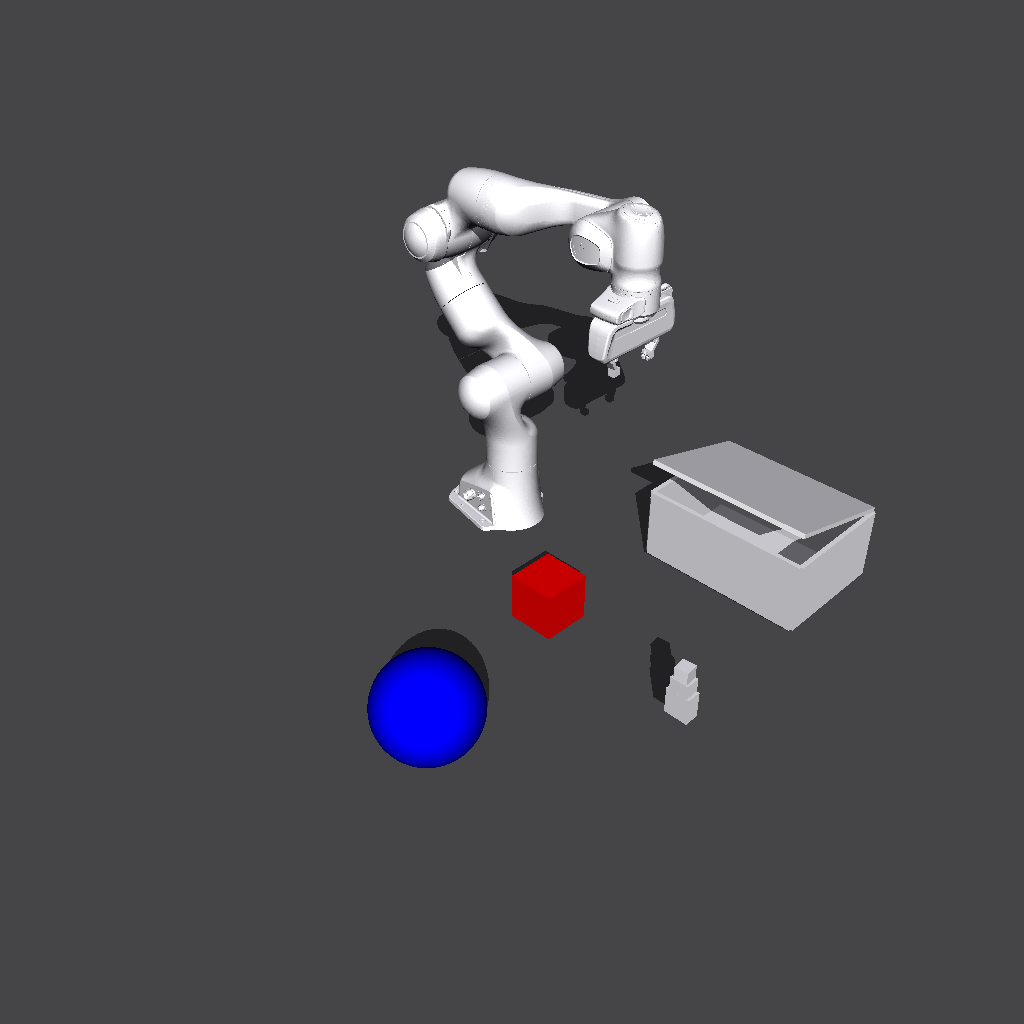
You will get the following image:#
Isaac Sim |
Isaac Gym |
Mujoco |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Genesis |
Sapien |
PyBullet |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Newton |
|---|
|
Code Highlights#
Object Configuration: Objects are added to scenario.objects with different types:
PrimitiveCubeCfg/PrimitiveSphereCfg: Simple geometric objectsRigidObjCfg: Static objects with physics propertiesArticulationObjCfg: Objects with joints (like the box_base)
Initial State Setup: Use handler.set_states() to position objects:
init_states = [{
"objects": {
"cube": {"pos": torch.tensor([0.3, -0.2, 0.05]), "rot": torch.tensor([1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])},
"sphere": {"pos": torch.tensor([0.4, -0.6, 0.05]), "rot": torch.tensor([1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])},
}
}]